Configure the e-mail client (Example: Thunderbird)
In order to use your e-mail account, you first need to configure your mail client. Here we provide you with step-by-step instructions .
We recommend using Mozilla Thunderbird as your e-mail client on your computer. You have to install this program on your device first. Various settings in the e-mail client also apply to other e-mail programs. E-mails can also be accessed via webmail with a web browser.
An e-mail account at consists of a username (m_name) and password. Your e-mail address is yourname@servus.at (or @your_domain_name). There is an incoming mail server and an outgoing mail server, which you need to configure for your e-mail client (e-mail program) to work.
Thunderbird Installation
Under Linux you can install it using the package manager or the software manager of your distribution. Use the following commands for specific distributions:
Debian, Ubuntu & co:
apt install thunderbirdRHEL, Centos, Fedora, … :
yum install thunderbirdor
dnf install thunderbirdWindows and OSX: You can install Thunderbird manually by downloading it from https://www.thunderbird.net/ or via package managers such as winget or homebrew.
Terminology: IMAP, POP3, SMTP
When configuring your e-mail program, terms appear that are important to understand, because they affect how you retrieve e-mail from our server. The SMTP protocol (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is used to feed and exchange e-mails. IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) and POP3 (Post Office Protocol Version 3) are available as protocols for retrieving e-mail from our mail server.
By choosing one of the two receiving protocols, you define the way you work with your e-mail correspondence. Whether you use IMAP or POP3 to fetch your mails depends mainly on your e-mail usage.
IMAP works in a way that users can leave their emails, folder structures and settings on the mail servers. The clients access the information on the servers directly online. An IMAP user keeps his/her mails on the servers and, even across multiple and different clients, always has uniform access. This is usually what you would want since you can access your emails from different machines and clients without worrying about local backups.
With POP3, on the other hand, after logging on to the mail server, all e-mails are downloaded from the mail server to the client. If you have configured it this way, they will be deleted from the mail server and will only be available on your client. So you cannot access your mails from a second device.
In short: If you would like to access your email from different devices, you can use IMAP. If you only use one device to read and send e-mail, you can use POP3, but you have to take care of backing up & locally storing your emails.
If you are unsure: You should use IMAP.
Thunderbird Configuration
The first time you start Thunderbird you will be asked for your e-mail address. Then the program automatically tries to find the appropriate settings for your e-mail account.
When adding a new account:
- First fill out your name, email address and password sections.
- Click Configure manually… at the bottom.
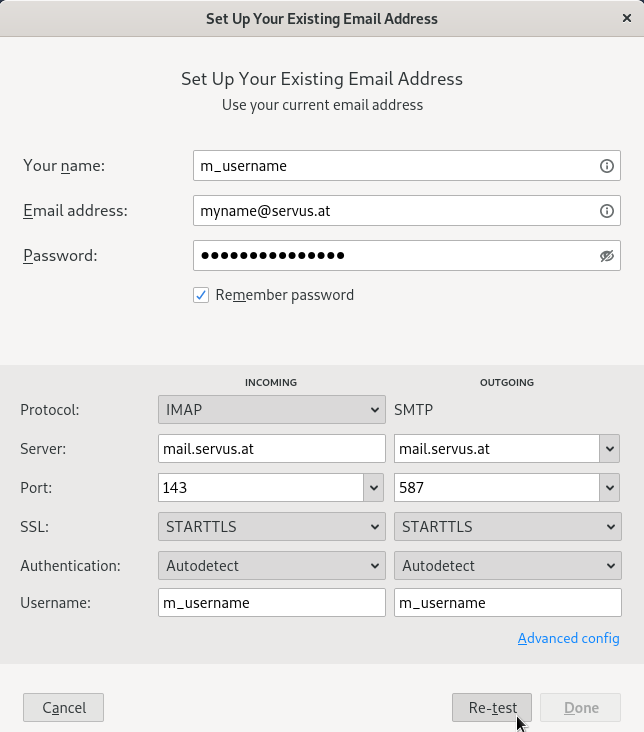
- Fill out the settings for INCOMING and OUTGOING with the information below:
INCOMING
Protocol: IMAP
Server: mail.servus.at
Port: 143
SSL: STARTTLS
Authentication: Autodetect
Username: m_usernameOUTGOING
Protocol: SMTP
Server: mail.servus.at
Port: 587
SSL: STARTTLS
Authentication: Autodetect
Username: m_usernameIf you are experiencing problems with receiving or sending emails in your email client (e.g. Thunderbird), please check the server settings again first, especially those of the outbox server. Here you can find the necessary information.
If problems still occur, this may be caused by installed antivirus programs or the firewall.
To check this, you can temporarily deactivate the antivirus program. If the sending process then works, the manufacturer can normally provide information on how to add exception rules for the email client.
The same procedure can be followed with the firewall. Here are the commands for the most common operating systems. If the firewall turns out to be the culprit, exception rules can be added to the firewall.
Ubuntu, Debian
sudo systemctl stop ufwTo see whether the firewall is active or not, use the following command.
sudo ufw status systemctl status firewalldFedora, CentOS
sudo systemctl stop firewalldTo see whether the firewall is active or not, use the following command.
sudo systemctl status firewalldWindows: Official Windows Support
MacOS: Official Apple Support
If all e-mails have been deleted by mistake, a simple e-mail to office@servus.at is sufficient and we will restore your mail account.